A protocol is therefore a set of rules that define how different systems communicate with each other. The difference between the OSI model and TCP/IP is the subject of this article.
In the case of computer networks, protocols define how data is transferred from one system to another. In this article, I will explain the difference between the TCP/IP and ISO models.
The ISO model
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a standard for networked communication between all computer systems. It is a model of communication between computers proposed by the ISO (International Organization for Standardization) which describes the functions necessary for communication and the organization of these functions.
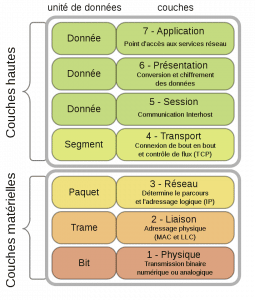
This model proposes a communication system composed of 7 different layers. The 7 layers defined by the OSI model are represented as follows:
| N° | Name | Units | Function |
| 7 | Application | Data | Access point to network services |
| 6 | Presentation | Data | Manages the encryption and decryption of data, converts machine data into data that can be used by any other machine |
| 5 | Session | Data | Inter-host communication, manages sessions between different applications |
| 4 | Transport | Segment | End-to-end connection, connectability and flow control; port concept (TCP and UDP) |
| 3 | Network | Package | Determines the data path and logical addressing (IP address) |
| 2 | Data linkage | Frame | Physical addressing (MAC address) |
| 1 | Physics | Bit | Transmission of signals in digital or analog form |
TCP/IP model
The TCP/IP suite, also known as the Internet protocol suite, is the set of protocols used to transfer data over the Internet. It is also often referred to as TCP/IP, after its first two protocols: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and IP (Internet Protocol).
The TCP/IP model is a realistic or practical approach to a network model where the OSI model is an idealized or theoretical model. Consequently, the TCP/IP model is used as the reference network model for the Internet.
This model proposes a communication system composed of 4 different layers. The 4 layers defined by the TCP/IP model are represented as follows:
| N° | Name | Units | Function |
| 4 | Application | Data | It is the communication layer that interfaces with the users, runs on the terminal host machines |
| 3 | Transport | Segment | It is responsible for the dialogue between the terminal hosts of a communication, applications will use TCP for reliable transport and UDP without this service. |
| 2 | Internet | Package | It allows to determine the best paths through the networks, globally identifies the interfaces, the routers transfer the IP traffic which is not intended for them |
| 1 | Network access | Frame, bit | It organizes the bitstream, physically identifies the interfaces, sets the media access method and places the bitstream on the physical media, switches, cables, NICs |
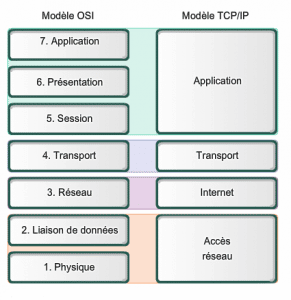
Difference between TCP/IP and ISO models
| TCP/IP model | ISO model |
| Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol | Open System Interconnect |
| 4 layers | 7 layers |
| It is a server/client model used for data transmission over the Internet. | It is a theoretical model that is used for the computer system. |
| Mainly used | In theory |